The Basics[]
Examiners love this topic.
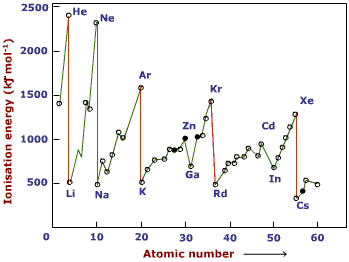
You should be able to account for the shape of this graph.
You should also be able to sketch it, or complete a missing section.
Exam Hints[]
- Each Period has lower ionisation energies than the previous one (see Period 2 Li to Ne compared to Period 3 Na to Ar) - this is because another shell has been added, making the electrons further from the nucleus and also shielding them more.
- The general trend within a period is up - this is because there is no additional shielding, the nuclear charge is increasing and (don't forget to mention) atomic size decreases across a period meaning that the electrons are getting closer to the nucleus.
- There is a drop from Be to B (and Mg to Al) - in both cases because the electron in Be (and Mg) came from an s orbital and in B (and Al) it came from a higher energy p orbital.
- There is a drop from N to O (and P to S) this is because the electronic structure of N ends with 2p3 and for O it is 2p4 - the fourth electron in the p subshell is forced to spin-pair. Putting two electrons in the same orbital causes some repulsion and makes it slightly easier to remove this electron
- You won't be asked about ionisation energies beyond element 18 because the trends within the D Block is less easily explained.
Videos[]

Ionization Energy and Atomic Radius
Ionization Energy and Atomic Radius